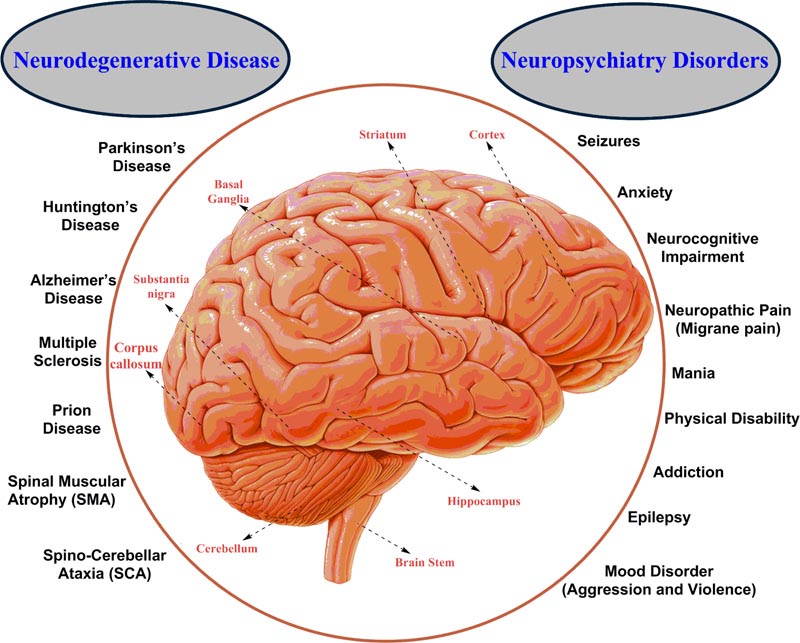
The human brain is one of the most complex and fascinating organs in the human body. However, it is also susceptible to numerous disorders that can severely impact a person’s quality of life. Traditional brain disorder treatment methods involve medication, therapy, and surgery. However, recent technological advancements have led to the development of a neurochip that can manage brain disorders more effectively.
What is Neurochip?
A neurochip, or a neural implant, is a device implanted in the brain to stimulate or suppress neural activity. The neurochip comprises electrodes placed in specific brain regions, allowing for precise targeting of neural activity. The neurochip sends electrical signals to the brain to modulate neural activity and alter brain function.

Applications of Neurochip
Neurochips have several applications in the management of brain disorders, including:
Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects the brain’s motor system. The symptoms of Parkinson’s disease include tremors, stiffness, and difficulty in movement. Neurochips can be used to stimulate the brain regions that are responsible for motor control, reducing the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
- Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a disorder characterized by seizures caused by abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Neurochips can detect and prevent seizures by monitoring neural activity in the brain and delivering electrical signals to suppress abnormal activity.
- Depression
Depression is a mental disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. Traditional methods of treating depression include medication and therapy. However, neurochips can be used to stimulate specific regions of the brain that are responsible for mood regulation, reducing the symptoms of depression.
- Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects memory and cognitive function. Neurochips can be used to stimulate the brain regions responsible for memory and cognitive function, improving the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease.

Advantages of Neurochips
- Precise Targeting
Neurochips allow for precise targeting of neural activity, reducing the risk of damaging healthy brain tissue. This is particularly important in managing brain disorders, where specific brain regions need to be targeted.
- Customizable
Neurochips can be customized to meet the individual needs of the patient. The electrodes can be placed in specific brain regions, and the electrical signals can be adjusted to provide optimal stimulation.
- Minimally Invasive
Neurochips are minimally invasive, meaning that they do not require surgery. The electrodes can be inserted into the brain through a small incision, reducing the risk of complications.
- Long-Term Management
Neurochips can provide long-term management of brain disorders. The electrodes can be implanted in the brain and left in place for extended periods, allowing continuous monitoring and stimulation.
- Efficiency, scalability, and versatility
Neurochips function by extracting neural biomarkers – patterns of electrical signals associated with certain neurological disorders – from brain waves. It then classifies the signals and indicates whether they herald an impending epileptic seizure or Parkinsonian tremor. If a symptom is detected, a neuro-stimulator is activated on the chip, sending an electrical pulse to block it.

According to research, the unique design of neurochips provides the system with an unprecedented level of efficiency and versatility when compared to the state-of-the-art. The chip has 256 input channels, compared to 32 in previous machine-learning-embedded devices, allowing the implant to process more high-resolution data. Because of the chip’s area-efficient design, it is also tiny (3.48mm2), providing great potential for scalability to more channels. Neuro-chips are also highly energy efficient due to incorporating an ‘energy-aware’ learning algorithm, which penalizes features that consume a lot of power.
Challenges of Neurochips
Following are the common challenges that are faced due to the use of neurochips:
 Cost: neurochips are expensive to develop and manufacture, making them inaccessible.
Cost: neurochips are expensive to develop and manufacture, making them inaccessible.- Ethical considerations: the use of neurochips raises ethical considerations of modifying brain function and the potential for abuse.
- Risk of complications: although neurochips are minimally invasive, there is still a risk of complications, such as infection or bleeding.
- Limited research: the use of neurochips is still in its early stages, and there is limited research on the long-term effects of their service.
Conclusion
Neurochips offer a promising new approach to the management of brain disorders. They provide precise targeting of neural activity and can be customized to meet the patient’s individual needs. In conclusion, neurochip development has opened up a new frontier in managing brain disorders.
While challenges are associated with using this technology, such as cost and ethical considerations, the benefits of precise targeting, customization, and long-term management cannot be overlooked. With continued research and development, neurochips have the potential to revolutionize the treatment of brain disorders and improve the quality of life for millions of people worldwide.